Synchronisation with continental Europe
Synchronisation press releases 
Current situation
The Baltic states’ electricity system is part of the unified Russian electricity system, which constitutes a geopolitical and energy security risk. This is due to the fact that Russia controls one of the most important parameters of our electricity system – the frequency – and thus has the ability to influence the functioning of the system in the Baltic states.
Why synchronization?
First of all, the transition to synchronous operation with the continental Europe frequency area lessens the risk that dependence on the Russian energy system and frequency area could be used against us.
Secondly, the Baltic states are politically and socioeconomically part of Western Europe, which makes it completely logical that the electricity system is likewise part of the continental Europe frequency area. This would reduce the risks related to controlling the system and improve energy security for individuals and businesses in Estonia.
Besides energy security, better integration of Estonia with the European system would improve the international competitiveness of the local economy. In the course of synchronization, new markets and products will arise alongside existing electricity markets, and this will increase the opportunities for local electricity producers to sell electricity.
Synchronization in brief:
How does synchronization take place?
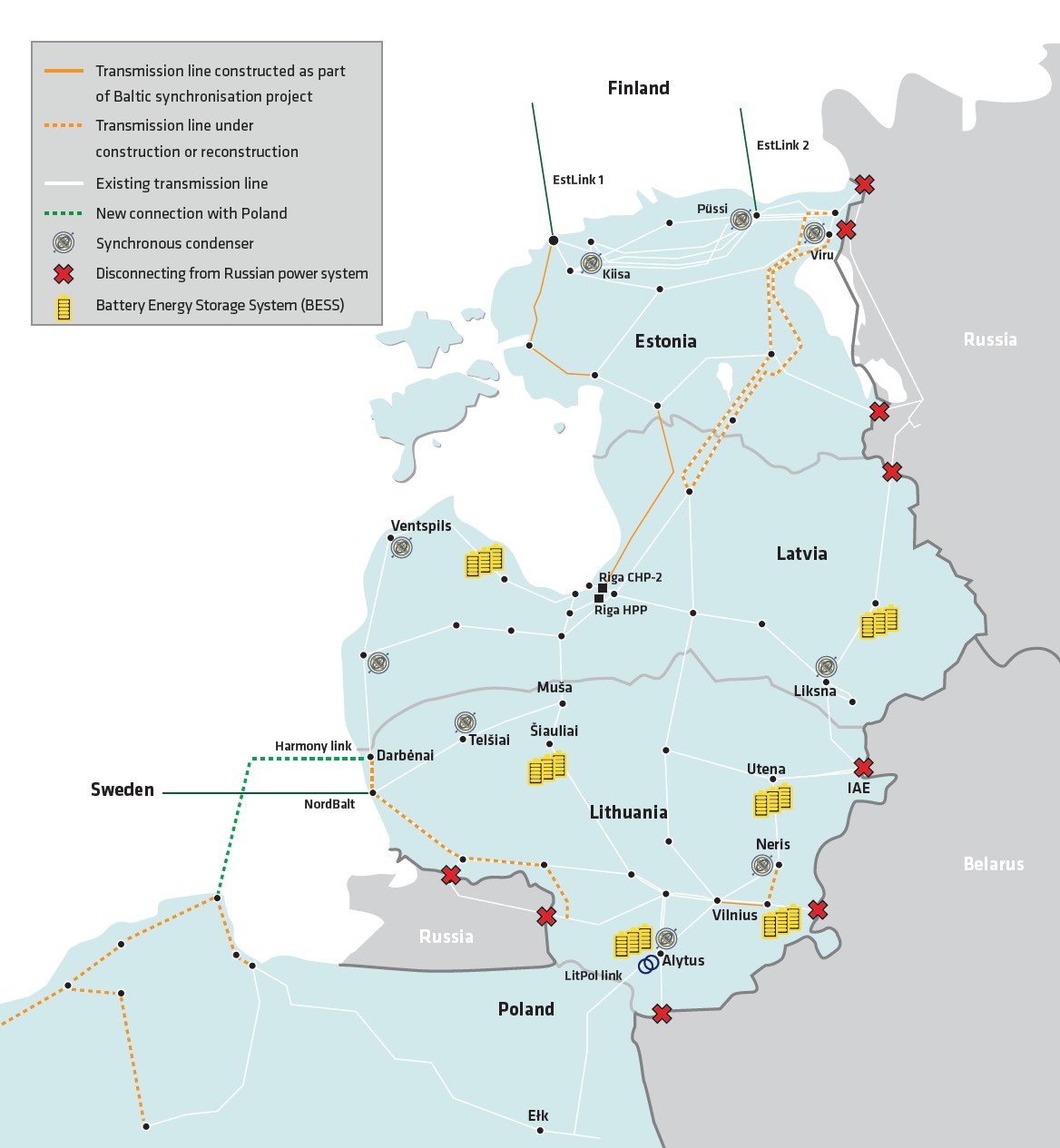
To mitigate risks and expand the market, we have started activities to decouple the Estonian, Latvian and Lithuanian electricity systems from the Russian system and at the beginning of 2025, join the continental Europe power grid and the corresponding frequency area. Since synchronization is a joint effort by the three Baltics and Poland, it is key for the projects needed for this to be completed in all countries pursuant to the agreed schedule. Activities related to synchronization have extremely high priority for Elering in order to ensure that all projects are completed on time.
During synchronization, the Baltics will reinforce their power grids and connections between each other. Elering will renovate the powerful 330-kilovolt power lines running from the Narva area to Latvia via near Valga. Similar reinforcements will be made to the Latvian and Lithuanian electricity systems.
To ensure frequency stability, the synchronous condensers will be established to add inertia to the system, and the electricity system, IT systems and existing direct-current connection control systems will be renovated.
Besides new infrastructure and systems, synchronization will also result in interoperability between Baltic states’ control centres and create additional know-how for independent control of the power grid.
Project funding
Synchronization will cost the Baltic state and Poland about 1.6 billion euros, of which Estonia’s share is 298 million euros. The investments will fall into three stages, and due to the high priority status accorded by the European Commission, 75% of the funding will come from the Connecting Europe Facility (CEF). The remaining 25% of the investments needed will come from the Congestion Income Fund, an ad hoc fund established in Estonia.
The total sum of the investments in the first stage of the funding in the Baltic states is approximately 430 million euros. In the first phase in Estonia, domestic power grids will be renovated and one synchronous condenser will be built. Similarly to Estonia, domestic network connections will be improved and synchronous condensers built in Latvia and Lithuania as well.
The volume of investments in the second stage in Baltics and Poland is approximately 700 million euros, which includes the establishment of two synchronous condensers in Estonia. The investments will fund the establishment of synchronous condensers in the other Baltic states and a connection between Lithuania and Poland along with the necessary network reinforcements.
The total sum of the investments in the third stage in the Baltic states is approximately 230 million euros. The investment objects in the third phase in Estonia is the renovation of the IT, control and monitoring systems in the control centre, renovation of the control and supervisory system of the Estlink 1 and 2 submarine cables and raising the operational continuity of substations. In the other Baltic states and Poland, the third-stage funds will be used to perform renovations of high-voltage lines, further development of substations, construction of battery-based energy storage systems in Latvia and renovations of IT systems.
A total of about 30 investment objects will be funded in Estonia as part of synchronization.
Benefits for market participants
Synchronization will provide electricity producers and traders with a larger and more flexible market, which allows new types of energy market products and services to be offered. Since the Lithuania-Poland undersea cable to be established is meant to handle commercial electrical flows, electricity producer will have new business opportunities and export potential will improve. Besides the existing ones, new markets will develop, increasing electricity producers' options for selling electricity. Since as of 2022, there is no more electricity trading with Russia and Belarus, access to new markets is of key importance for market participants. TSOs are introducing new products to the electricity markets, giving market participants an opportunity to offer new services. Such services include a reserve for maintaining frequency and a reserve for automatically restoring frequency. TSOs will involve the market participants in introducing new products to meet their possibilities and expectations.
Benefits for consumers
For consumers, synchronization will above all ensure better security of supply as well as a sense of security that Estonia itself has full control of its electricity system, not Russia. In addition, European Union investments can be used to renovate the depreciated high-voltage lines, for which no additional resources will have to be raised; thus there would be no need to hike network fees. The transition from one frequency area to another will take place imperceptibly for end consumers and the quality of the network connection and uptime will improve.
Environmental impact
Estonia is acceded to carbon neutrality goals aimed at slowing global climate change. It is thus not conceivable to invest in renewable energy at home while consuming electricity of unknown environmental footprint from third countries. Carbon emissions will not decrease if the emissions merely are diverted outside the border of the EU. Synchronization will put an end to the risk of possible carbon leakage and improve the possibilities for generating electricity from renewable sources.
Readiness for extraordinary synchronization
The Baltic states and Poland have prepared for a situation where desynchronization from Russia must take place under extraordinary circumstances. To this end, Elering has agreed with the TSOs of the Baltics and Poland on specific actions and protocols for joining the continental Europe synchronous area as securely and rapidly as possible. This will ensure security of supply for consumers and protect countries’ security and economic interests. The emergency synchronization would also be imperceptible for consumers and take place in a matter of hours.
The basic outline of the desynchronization process would be as follows:
- The Baltic states are desynchronized from the Russian and Belarusian (IPS/UPS) frequency area, as a result of which the inertia and frequency of the Baltic states’ electricity system is not overseen from Russia.
- The Baltic states are in island mode, where the necessary inertia is ensured by local capabilities and means.
- The Baltic states are synchronized with the continental European frequency area.
Elering is in constant cooperation with Latvian, Lithuanian and Polish partners to raise readiness for emergency synchronization. The following actions have been taken for this purpose:
- 400/330 kV alternating current transformers have been installed in Alytus substation in Lithuania, which ensure technical readiness for emergency synchronization via LitPol link in a matter of hours.
- Agreements have been reached with Nordic TSOs for obtaining frequency support via DC connections through the Estlink 1, Estlink 2 and NordBalt cables.
- Regular training at TSOs’ control centres is carried out for a situation where emergency desynchronization takes place by Russia and Belarus.
- A legal and technical framework for emergency synchronization with continental Europe has been developed.
Risk mitigation
From the perspective of synchronization, construction and supply contracts for most critical infrastructure projects have been concluded and activities have begun, due to which a number of risks arising from interruption of soppy chains or commodities price increases have not materialized or their impact has been low. The probability of potential risks materializing and their impact are assessed at Elering constantly to prevent and reduce negative impact to project budgets and timetables of the actions necessary for synchronization.
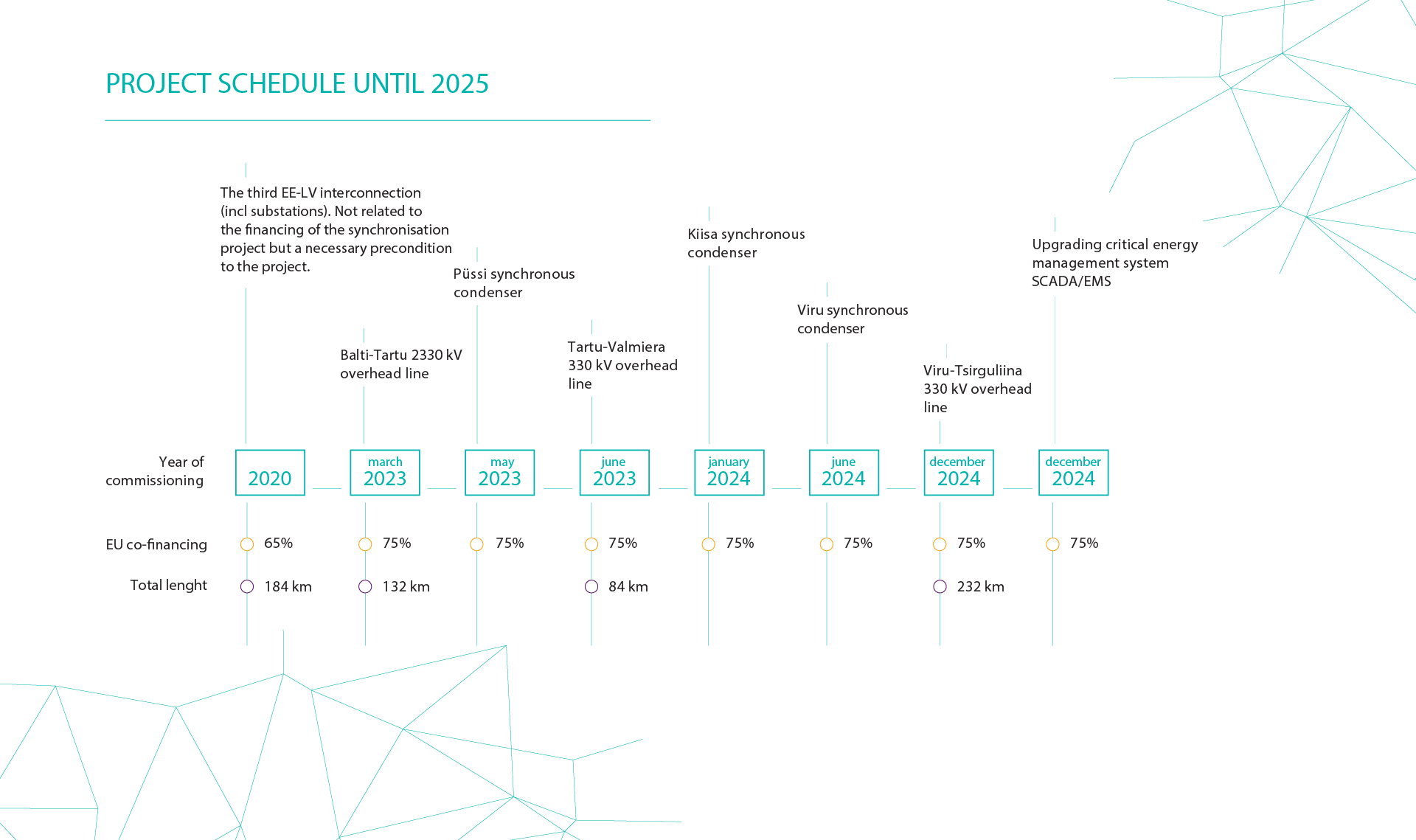
Overview of projects:
(updated in January 2024)
Elering is establishing synchronous condensers at Püssi, Kiisa and Viru substations and they will be used for controlling frequency.
The reason for this is that based on studies and market changes in electricity, after decoupling from the Russian frequency area, the Baltic electricity system will not have the necessary degree of inertia to ensure frequency stability and the required speed of change in frequency.
In the Estonian context, the adoption of synchronous condensers means that there will be a less of a need to keep the Narva power plants’ units operational outside the market for the purpose of ensuring frequency, something that would entail significant expenses.
Elering is establishing synchronous condensers at Püssi, Kiisa and Viru substations. The synchronous condensers will be used for controlling frequency. The synchronous condensers’ function is to add inertia to the system to slow down the change in frequency and allow the subsequent measures to be implemented in the frequency control process, in the case of accidents for example. The synchronous condensers to be established are highly reliable and also provide support to the network in the form of short-circuit power and reactive energy compensation. A total of nine synchronous condensers will be established in the Baltics. In Estonia, the synchronous condensers will be built by the Estonian branch of Siemens Energy Oy and Siemens Energy Global GmbH & Co. KG. All of the synchronous condensers to be built in Estonia are identical in design and operating principles, which will ease maintenance and make possible to ensure construction of the equipment in as short a timeframe as possible.
Püssi synchronous condenser station
General construction at Püssi synchronous condenser station is almost completed. The generator, rotor and transformer have arrived in Estonia from a plant in Germany . Reliability testing will be performed at the end of this year and the station will enter use in April 2023.
Kiisa synchronous condenser station
The second synchronous condenser station will be built at Kiisa, where the site preparation and design work has begun. The construction of the necessary equipment has started and the station will be completed by January 2024.
Viru synchronous condenser station
The third and final synchronous condenser station in north-eastern Estonia will be completed in June 2024. Similarly to Kiisa, site preparations and design work have begun and Siemens is building compensator components.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| The beginning of the procurement process | 18.05.2020 |
| Signing the contract | 16.12.2020 |
| Start of work at Püssi station | 01.01.2021 |
| Start of work at Kiisa station | 01.05.2022 |
| Start of work at Viru station | 01.05.2022 |
| End of work at Püssi station | 01.05.2023 |
| End of work at Kiisa station | 01.01.2024 |
| End of work at Viru station | 01.06.2024 |
Transport and installation of the Viru synchronous condenser generator, September 2023
Transport of the transformer of Viru synchronous condenser, September 2023:
Kiisa synchronous condenser generator preparation for installation in May 2023:
Transport of the generator of Kiisa synchronous condenser from Paldiski harbor to Kiisa in May 2023:
Arrival of the main equipment of Kiisa synchronous condenser in April 2023:
Arrival of the equipment of Püssi synchronous condenser in June 2022:
Elering will renovate the old overhead lines and line corridors to increase the capacity of the existing lines.
Namely, desynchronization from the Russian system will mean no more possibility of sending a part of the capacity flows through the Russian electricity system – the entirety of the capacity transmitted between Estonia and Latvia will be transmitted over lines connecting Estonia and Latvia. Renovating the lines will preserve capacity at current levels and help to avoid restrictions on north-south transit. After synchronization, the new network will be as least as strong a network as before and there will be no more third-county influence on trading between markets in the Baltic states.
Elering chose to renovate rather than build new lines. This was in order to ensure timely completion of projects, reducing potential expenses. While the lines are being renovated, it is important to keep in mind that transmission capacity must be guaranteed in every situation – if a malfunction occurs on some of the lines (an n-1 situation). Due to this, all lines cannot be renovated at the same time.
The lines L300/L301 along with L353/L354 make up a parallel line corridor between Estonia and Latvia. Renovating the lines is necessary to strengthen connections between the Estonian electricity system and the rest of the electricity system, creating preconditions for synchronous operation with the European electricity system. The lines have a key role in allowing lower-price producers to access the Estonian market. Since the Kuna 330 kV lines in Estonia were built in the 1950s and 1960s, their lifespan will start running out and there is a great need for renovation.
Renovating the 330 kV Balti-Tartu overhead line
The renovation of the Balti-Tartu 330 kV overhead line began in 2020. The renovated line entered use in February 2023.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 02.01.2019 |
| Signing the contract | 30.11.2020 |
| Start of the construction works | 12.04.2021 |
| End of the construction works | 01.03.2023 |
Dismantling of the Balti-Tartu (L300) line:
Erecting the pylon in Iisaku:
Renovation of the 330 kV Tartu-Valmiera (L301) overhead line
Renovation of the 330 kV Tartu-Valmiera overhead line began in autumn 2021. The line was completed in May 2023.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 02.01.2019 |
| Signing the contract | 30.11.2020 |
| Start of the construction works | 20.09.2021 |
| End of the construction works | 01.06.2023 |
Renovating Balti-Tartu and Tartu-Valmiera 330kV overhead lines, 2021-2023:
Renovating the 330 kV Viru-Tsirguliina overhead line
Similarly to the Balti-Tartu-Valmiera line, the 330 kV line from Tsirguliina-Valmiera must also be renovated. Already before the beginning of the synchronization related activities, a 11.48 km stretch of the Tsirguliina-Valmiera (L354) line on Estonian soil was renovated in 2015. During the renovation, the lead wire was replaced and gauge maintenance was carried out.
A contract for services was concluded for the Viru-Tsirguliina (L353) renovation work and geological, geodetic and design work is under way along the corridor. The part of the line on Estonian soil will be completed by the end of 2024. The total renovation of the line on Latvian territory is planned for the same period as the Estonian part of the line.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 01.08.2020 |
| Signing the contract | 02.06.2021 |
| Start of the construction works | 01.06.2023 |
| End of the construction works | 31.12.2024 |
The Estlink 1 and Estlink 2 submarine cables are among the most important connections linking the Baltics to the Nordics, which offer our electricity system support in regulating frequency.
Due to the requirements and functionalities related to synchronization, it is necessary to renovate the control and oversight systems of substations on the land on both sides of the submarine cable. As part of synchronization, the hardware and software of Estlink 1 and 2’s control systems and the reliability of the substations will be increased, installing new relays, transformers and power supply systems. The necessary renovations will be performed in both Estonia and Finland.
ESTLINK 1 TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 30.07.2022 |
| Signing the contract | 21.11.2023 |
| End of the works | 30.09.2027 |
ESTLINK 2 TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 01.03.2023 |
| Expected end of the works | 31.12.2025 |
Projects and investments necessary for synchronization do not include solely infrastructure projects but the electricity control system’s IT and communication capabilities also need development.
In this context, the electricity system’s planning and control systems (SCADA/EMS) used to plan, monitor and control changes in the electricity system remotely will be renovated. As a result of the upgrade, the control centre’s ability to assess and control the electricity system in real time will be improved.
It is also important that the real-time measurement data on monitoring the electricity system’s stability and frequency control and data exchange are high in quality, reliable and guaranteed continuously. To this end, data communication and monitoring systems in critical substations will be replaced with new and more reliable equipment, which ensure constant transmission of data related to voltage, current and frequency.
In addition, various output and demand forecasting systems will be renovated, new balancing management software and downtime planning software will be procured and implemented.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 01.12.2021 |
| Signing the contract | 01.02.2022 |
| Start of development work | 01.02.2022 |
| End of development work | 01.12.2025 |
Elering is establishing synchronous condensers at Püssi, Kiisa and Viru substations and they will be used for controlling frequency.
The reason for this is that based on studies and market changes in electricity, after decoupling from the Russian frequency area, the Baltic electricity system will not have the necessary degree of inertia to ensure frequency stability and the required speed of change in frequency.
In the Estonian context, the adoption of synchronous condensers means that there will be a less of a need to keep the Narva power plants’ units operational outside the market for the purpose of ensuring frequency, something that would entail significant expenses.
Elering is establishing synchronous condensers at Püssi, Kiisa and Viru substations. The synchronous condensers will be used for controlling frequency. The synchronous condensers’ function is to add inertia to the system to slow down the change in frequency and allow the subsequent measures to be implemented in the frequency control process, in the case of accidents for example. The synchronous condensers to be established are highly reliable and also provide support to the network in the form of short-circuit power and reactive energy compensation. A total of nine synchronous condensers will be established in the Baltics. In Estonia, the synchronous condensers will be built by the Estonian branch of Siemens Energy Oy and Siemens Energy Global GmbH & Co. KG. All of the synchronous condensers to be built in Estonia are identical in design and operating principles, which will ease maintenance and make possible to ensure construction of the equipment in as short a timeframe as possible.
Püssi synchronous condenser station
General construction at Püssi synchronous condenser station is almost completed. The generator, rotor and transformer have arrived in Estonia from a plant in Germany . Reliability testing will be performed at the end of this year and the station will enter use in April 2023.
Kiisa synchronous condenser station
The second synchronous condenser station will be built at Kiisa, where the site preparation and design work has begun. The construction of the necessary equipment has started and the station will be completed by January 2024.
Viru synchronous condenser station
The third and final synchronous condenser station in north-eastern Estonia will be completed in June 2024. Similarly to Kiisa, site preparations and design work have begun and Siemens is building compensator components.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| The beginning of the procurement process | 18.05.2020 |
| Signing the contract | 16.12.2020 |
| Start of work at Püssi station | 01.01.2021 |
| Start of work at Kiisa station | 01.05.2022 |
| Start of work at Viru station | 01.05.2022 |
| End of work at Püssi station | 01.05.2023 |
| End of work at Kiisa station | 01.01.2024 |
| End of work at Viru station | 01.06.2024 |
Transport and installation of the Viru synchronous condenser generator, September 2023
Transport of the transformer of Viru synchronous condenser, September 2023:
Kiisa synchronous condenser generator preparation for installation in May 2023:
Transport of the generator of Kiisa synchronous condenser from Paldiski harbor to Kiisa in May 2023:
Arrival of the main equipment of Kiisa synchronous condenser in April 2023:
Arrival of the equipment of Püssi synchronous condenser in June 2022:
Elering will renovate the old overhead lines and line corridors to increase the capacity of the existing lines.
Namely, desynchronization from the Russian system will mean no more possibility of sending a part of the capacity flows through the Russian electricity system – the entirety of the capacity transmitted between Estonia and Latvia will be transmitted over lines connecting Estonia and Latvia. Renovating the lines will preserve capacity at current levels and help to avoid restrictions on north-south transit. After synchronization, the new network will be as least as strong a network as before and there will be no more third-county influence on trading between markets in the Baltic states.
Elering chose to renovate rather than build new lines. This was in order to ensure timely completion of projects, reducing potential expenses. While the lines are being renovated, it is important to keep in mind that transmission capacity must be guaranteed in every situation – if a malfunction occurs on some of the lines (an n-1 situation). Due to this, all lines cannot be renovated at the same time.
The lines L300/L301 along with L353/L354 make up a parallel line corridor between Estonia and Latvia. Renovating the lines is necessary to strengthen connections between the Estonian electricity system and the rest of the electricity system, creating preconditions for synchronous operation with the European electricity system. The lines have a key role in allowing lower-price producers to access the Estonian market. Since the Kuna 330 kV lines in Estonia were built in the 1950s and 1960s, their lifespan will start running out and there is a great need for renovation.
Renovating the 330 kV Balti-Tartu overhead line
The renovation of the Balti-Tartu 330 kV overhead line began in 2020. The renovated line entered use in February 2023.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 02.01.2019 |
| Signing the contract | 30.11.2020 |
| Start of the construction works | 12.04.2021 |
| End of the construction works | 01.03.2023 |
Dismantling of the Balti-Tartu (L300) line:
Erecting the pylon in Iisaku:
Renovation of the 330 kV Tartu-Valmiera (L301) overhead line
Renovation of the 330 kV Tartu-Valmiera overhead line began in autumn 2021. The line was completed in May 2023.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 02.01.2019 |
| Signing the contract | 30.11.2020 |
| Start of the construction works | 20.09.2021 |
| End of the construction works | 01.06.2023 |
Renovating Balti-Tartu and Tartu-Valmiera 330kV overhead lines, 2021-2023:
Renovating the 330 kV Viru-Tsirguliina overhead line
Similarly to the Balti-Tartu-Valmiera line, the 330 kV line from Tsirguliina-Valmiera must also be renovated. Already before the beginning of the synchronization related activities, a 11.48 km stretch of the Tsirguliina-Valmiera (L354) line on Estonian soil was renovated in 2015. During the renovation, the lead wire was replaced and gauge maintenance was carried out.
A contract for services was concluded for the Viru-Tsirguliina (L353) renovation work and geological, geodetic and design work is under way along the corridor. The part of the line on Estonian soil will be completed by the end of 2024. The total renovation of the line on Latvian territory is planned for the same period as the Estonian part of the line.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 01.08.2020 |
| Signing the contract | 02.06.2021 |
| Start of the construction works | 01.06.2023 |
| End of the construction works | 31.12.2024 |
The Estlink 1 and Estlink 2 submarine cables are among the most important connections linking the Baltics to the Nordics, which offer our electricity system support in regulating frequency.
Due to the requirements and functionalities related to synchronization, it is necessary to renovate the control and oversight systems of substations on the land on both sides of the submarine cable. As part of synchronization, the hardware and software of Estlink 1 and 2’s control systems and the reliability of the substations will be increased, installing new relays, transformers and power supply systems. The necessary renovations will be performed in both Estonia and Finland.
ESTLINK 1 TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 30.07.2022 |
| Signing the contract | 21.11.2023 |
| End of the works | 30.09.2027 |
ESTLINK 2 TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 01.03.2023 |
| Expected end of the works | 31.12.2025 |
Projects and investments necessary for synchronization do not include solely infrastructure projects but the electricity control system’s IT and communication capabilities also need development.
In this context, the electricity system’s planning and control systems (SCADA/EMS) used to plan, monitor and control changes in the electricity system remotely will be renovated. As a result of the upgrade, the control centre’s ability to assess and control the electricity system in real time will be improved.
It is also important that the real-time measurement data on monitoring the electricity system’s stability and frequency control and data exchange are high in quality, reliable and guaranteed continuously. To this end, data communication and monitoring systems in critical substations will be replaced with new and more reliable equipment, which ensure constant transmission of data related to voltage, current and frequency.
In addition, various output and demand forecasting systems will be renovated, new balancing management software and downtime planning software will be procured and implemented.
TIMETABLE:
| Activity | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Beginning of the procurement process | 01.12.2021 |
| Signing the contract | 01.02.2022 |
| Start of development work | 01.02.2022 |
| End of development work | 01.12.2025 |